Non-market App Distribution
For IOS Apps
There are two cases which you want to distribute your applications outside the App Store:
- Testing Purpose: Before releasing your apps, you would want to test them as much as you can. Thus, you would want to distribute your apps to users (testers) by various ways besides the App Store.
- In-house Applications: The applications are made for internal uses (in a company or organization) only.
The differences between Apple Developer and Apple Developer Enterprise programs regarding apps distribution:
| Apple Developer Program | Apple Developer Enterprise Program | |
|---|---|---|
| Beta OS Releases | Yes | Yes |
| Ad Hoc Distribution | Yes | Yes |
| App Store Distribution | Yes | No |
| In-house Distribution | No | Yes |
| TestFlight Beta Testing | Yes | No |
| Team Management | No | Yes |
| App Analytics | Yes | No |
For more information about the differences between the two programs, please refer to Choosing a Membership.
There are two ways to distribute your pre-release apps for testing:
- using App Store Connect: it’s required iOS Developer Account and takes time since it needs approval from Apple Review prior to the distribution.
- using Ad Hoc distribution: it can be done with either iOS Developer and iOS Developer Enterprise accounts. Plus, it doesn’t require the approval from Apple Review.
In-house distribution is to securely distribute your iOS apps to your employees. In other words, you can distribute your app to any company devices. However, if you want someone outside of your company to test your app or restrict distribution to specific devices, you can use Ad Hoc distribution.
Ad Hoc distribution is to distribute your apps using Ad Hoc provisioning profile to registered devices up to 100.
Both types of distribution have the same ways for app installation. The difference is the provisioning profile.
There are several ways you can install your applications outside the App Store as shown in the following sections.
Install using Apple Configurator 2 (Mac Only)
- Install
Apple Configurator 2on your Mac from the App Store. - Connect your device to your PC.
- Open
Apple Configurator 2, select your device. If you device doesn’t appear here, please make sure that your device is successfully connected to your Mac.
Click on Add button and select
Appoption.
Select Choose from my Mac button and browse the
.ipafile. Then, the app will be installed on your device.
Install using Xcode
You can install your iOS app (.ipa file) via Xcode as follows:
- Connect your device to your PC.
- Open Xcode, go to Window → Devices .
- Then, the Devices screen will appear. Choose the device you want to install the app on.
- Drag and drop your
.ipafile into the Installed Apps as shown below: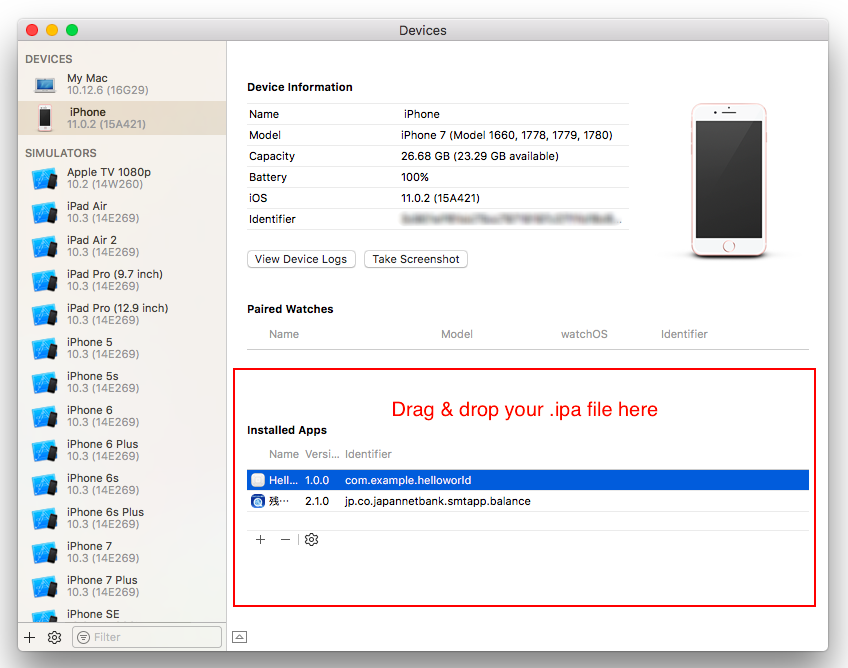
Install using iTunes
- Build your application with with debug or ad-hoc build. For more details about iOS build process, please refer to Building an iOS App.
- Download the
.ipafile after the build completes. - Open iTunes, go to
App library. - Drag and drop the downloaded
.ipafile into theApp library. - Connect your device to iTunes and go to your device apps.
- Click Install button of the app and click Sync button. See the example below:
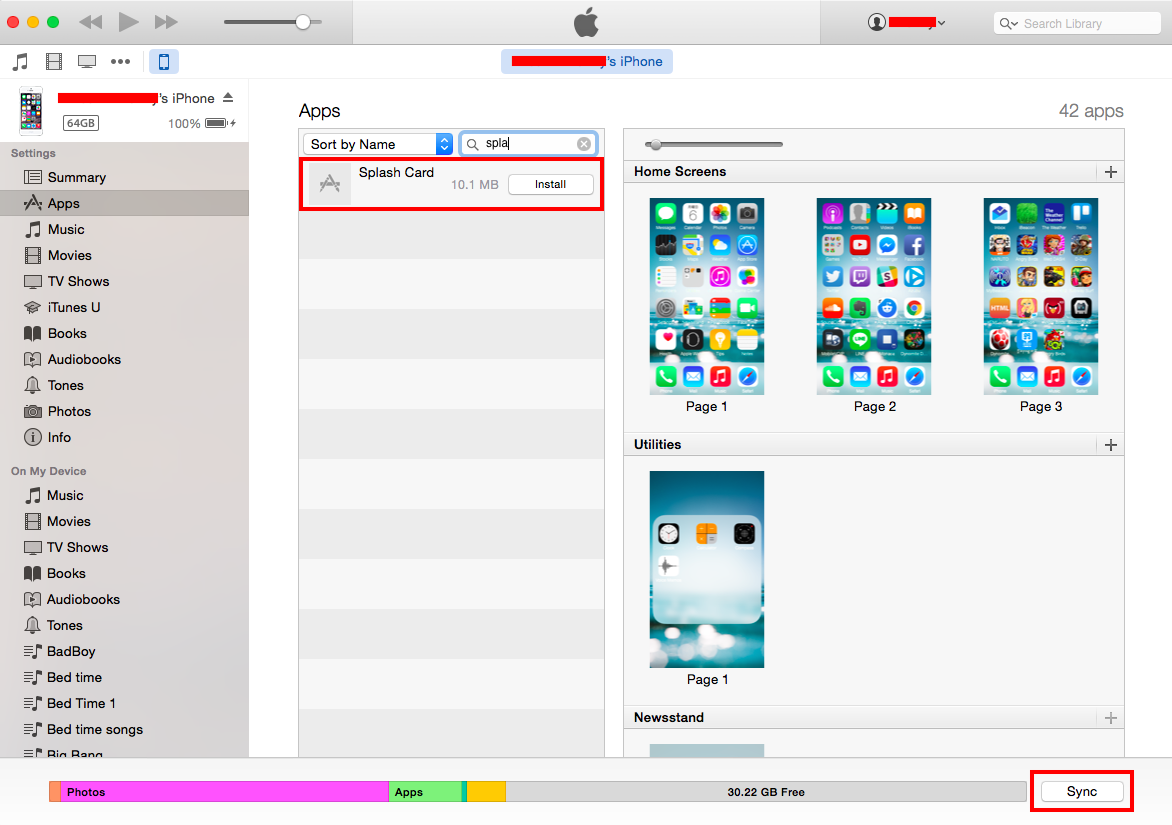
Install using OTA Deployment
OTA (Over-The-Air) Deployment enables you to install your built apps via HTTPS.
- Build your application with either debug, ad-hoc or in-house build. For more details about iOS build process, please refer to Building an iOS App.
- Download the
.ipafile after the build completes. - Upload the
.ipafile to the site you want. Create a
.plistfile for this built application. The.plistfile should look like this:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd"> <plist version="1.0"> <dict> <key>items</key> <array> <dict> <key>assets</key> <array> <dict> <key>kind</key> <string>software-package</string> <key>url</key> <string>https://www.anysite.com/application/your_app.ipa</string> </dict> </array> <key>metadata</key> <dict> <key>bundle-identifier</key> <string>com.example.helloworld</string> <key>bundle-version</key> <string>1.0.0</string> <key>kind</key> <string>software</string> <key>title</key> <string>HELLO</string> </dict> </dict> </array> </dict> </plist>While creating.plistfile, please pay attention to these points:.plistfile must be accessed via https protocol.- update bundle-identifier with the App ID.
- specify correct path to the
.ipafile.
Upload the
.plistfile to the site you want. Make sure this file must be accessed via HTTPS protocol.Create a webpage embedded the link to the uploaded
.plistfile using specialitms-services://protocol. See blow example:<a href="itms-services://?action=download-manifest& url=https://www.anysite.com/application/your_app.plist"> Download </a>After you get the link, use your device to access the link. Then, you will be prompted to install the application. See below example:
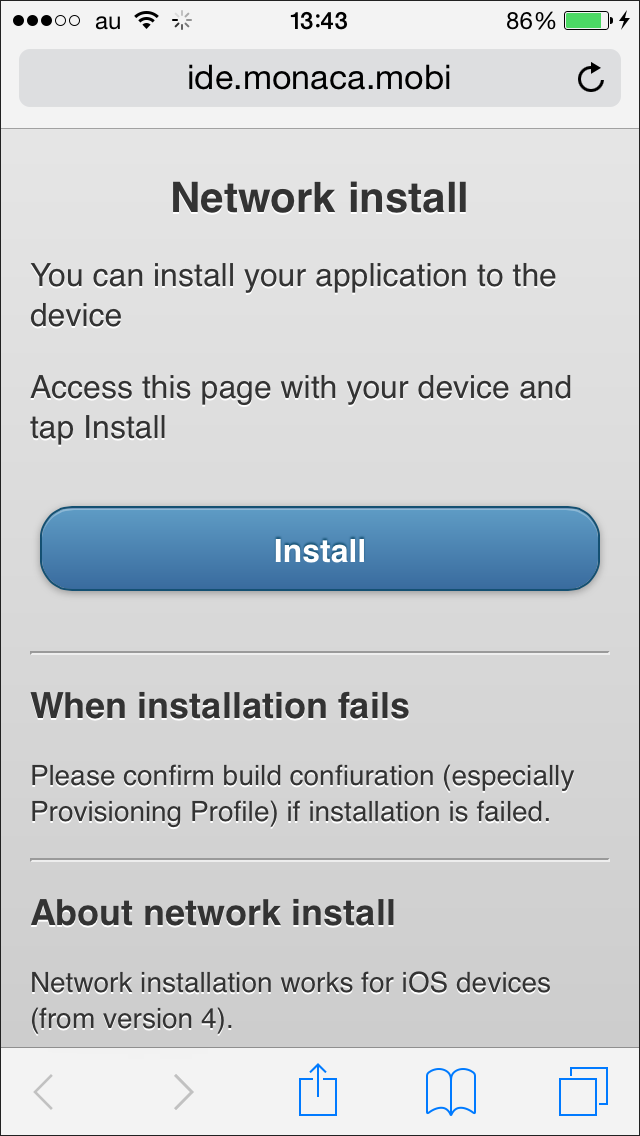
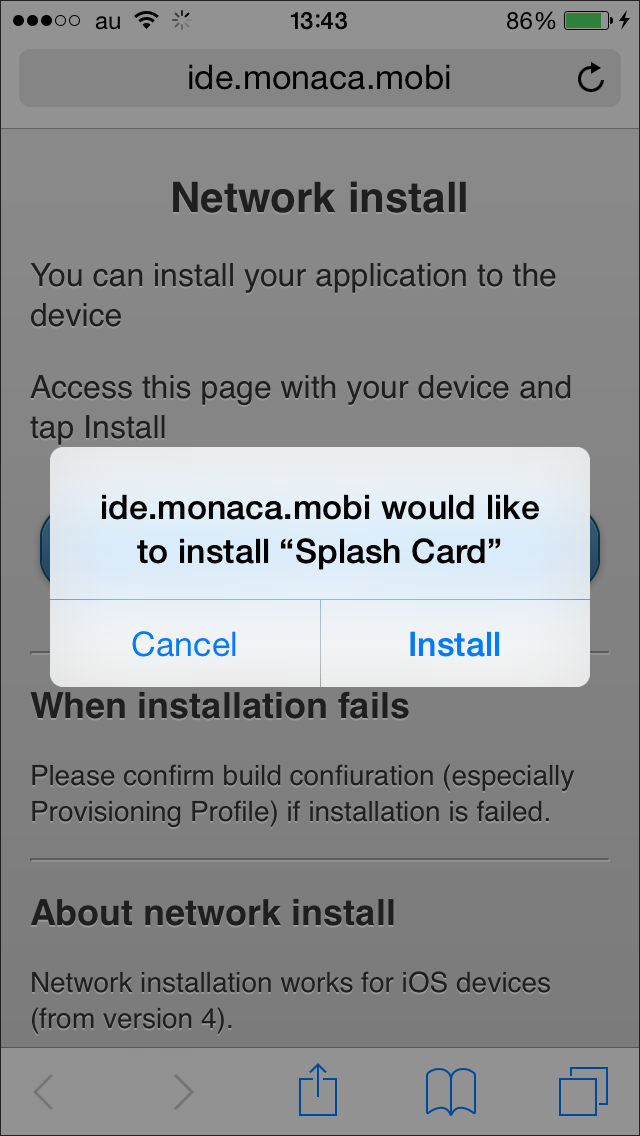
For Android Apps
There are two cases which you want to distribute your applications outside the offical markets such as Google Play Store, Amazon AppStore and so on:
- Testing Purpose: Before releasing your apps, you would want to test them as much as you can. Thus, you would want to distribute your apps to users (testers) by various ways besides the official markets.
- Personal/Internal Purpose: The applications are made for your own personal uses or just for internal uses.
Install using ADB command
ADB (Android Debug Bridge) is a tool enabling you to use various terminal commands to your phone.
Prerequisite:
- install Android SDK on your computer
- locate the ADB path after Android SDK installation
- enable USB Debugging and allow installation of apps from sources other than the Play Store on your device.
In order to install your built app via ADB command:
- Build your application with debug build. For more details about Android build process, please refer to Building for Android.
- Download the
.apkfile after the build completes. - Plug your device via USB to your computer.
Run below command on your computer in command window. Make sure to use the correct path to your
.apkfile.adb install foo.apk
Install using Direct Link
This is simply an installation through direct link to your .apk file:
- Build your application with debug build. For more details about Android build process, please refer to Building for Android.
- Download the
.apkfile after the build completes. - Upload the downloaded file to any sites you want.
Go the link of the uploaded file from your device. Then, you will be prompted to install the applicaiton.
Please make sure make these settings on your device beforehand:- enable USB Debugging.
- allow installation of apps from sources other than the Play Store.
See Also:

